
What is Earthquake?

Earthquake is a result of a sudden fault motion. Earth's surface layers are composed of a small number of moving plates. Their relative motion generates sudden fault motions from time to time. That is earthquake.
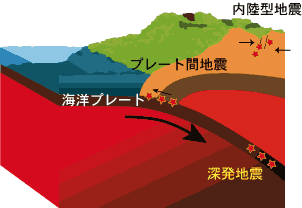
Earthquakes are classified into two major groups. One is the so-called inter-plate earthquakes that occur at plate boundaries (focal depth, less than ~70 km) and the other is the so-called intra-plate earthquakes that occur within a plate. The latter is further classified into shallow inland earthquakes (focal depth, less than ~30 km) and deep earthquakes (focal depth, to ~670 km).
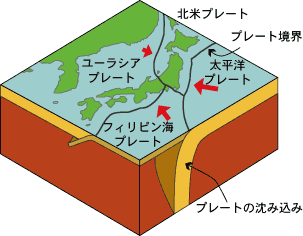
There are 4 plates in the region of Japan Islands. Pacific plate and Philippine Sea plate are subducting under the Japan Islands. This subduction zone causes about 10 % of the earthquakes all over the world.
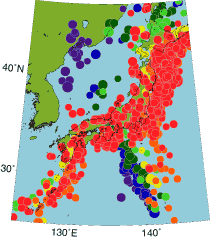
Earthquakes occur almost everywhere in the Japan Islands region. However, most of them are inter-plate earthquakes. They occur at the plate boundaries off-shore, and their focal depth becomes deeper along the slabs of oceanic plates subducting. Deep earthquakes (focal depth, more than ~100 km) occur within slabs and are relatively small in number. Deep earthquakes in Northeast Japan arc occur even under Siberia while thoese in Izu-Bonin arc are limited within a narrow zone. This difference is due to the difference in the dip of Pacific and Philippine Sea slabs subducting.

