- Space-temporal structure and global distribution of inhomogeneities in neutral atmosphere and ionosphere;To realize such a research, the scientific payload of the MICROSAT has to provide the measurements of following parameters:
- Global structure and dynamics of quasi-stationary electric currents, electric and magnetic fields;
- Wave structures and turbulences at different spatial and temporal scales;
- Synchronous experiments with ground support facilities - both active and passive ones.
- Neutral gas and plasma parameters - concentrations, temperatures;Intended payload structure to realize such measurements is given in the Table below.
- Vectors of DC-ELF-VLF electromagnetic field and ELF-VLF plasma current fluctuations (waveforms);
- Total electron content (TEC);
- Spectrum of ionospheric plasma waves.
| 1. Wave probes WP (3 pieces) | Electric current density J: Frequency range 0.1 Hz - 40 kHz Noise 10-12A/cm2Hz1/2 Magnetic field B: Frequency range 0.1 Hz - 40 kHz Noise 10-14 T/Hz1/2 Electric potential ��: Frequency range 0.1 Hz - 40 kHz Noise 10-6 V/Hz1/2 | Power: �E0.25 W Weight: 0.225 kg | Lviv Centre of Institute for Space Research (LCISR), Ukraine |
| 2. Electric probe EP | Electric potential: Frequency range DC - 200 kHz Noise 10-6 V/Hz1/2 | Power: �E 0.15 W Weight:�E 0.2 kg | LCISR, Ukraine |
| 3. Radiofrequency analyzer RFA | High frequency variations, electric component. Frequency range 0.1 - 15 MHz | Power: �E 5 W Weight: �E 4 kg (including antenna) | Space Research Centre, Poland |
| 4. Sensor of neutral and charged particles DN-DE | Density and temperature neutral prtcl. Nn: 105 - 1012 cm-3 charged prtcl. Ni: 103 - 1011 cm-3 electron temp. 0.1 - 1.5 keV | Power: �E 2 W Weight:�E 3 kg | Institute of Technical Mechanics, Ukraine |
| 5. DC flux-gate magnetometer FGM | Frequency range DC - 1 Hz
Resolution 0.01 nT | Power: �E 0.3 W Weight:�E 0.3 kg | LCISR, Ukraine |
| 6. TEC meter | Frequency L1 = 1217 - 1265 MHz L2 = 1565 - 1615 MHz 20 channels | Power: 2.4 W Total Weight: �E1.34 kg | IZMIRAN, Russia |
| 7. DPU | Input information rate, Mb/c, 100 Output information rate, Mb/c, 64 Onboard memory, up to 28 GB | Power: �E 4 W Weight: �E 1.5 kg | LCISR, Ukraine |
The initial sketch of MICROSAT spacecraft (SC) is given below. Its service systems have to provide:
- GPS determination of SC positioning with error about �E20 m;
- SC attitude control within 5 deg.;
- SC attitude determination with the error no more than �E0.2 deg.
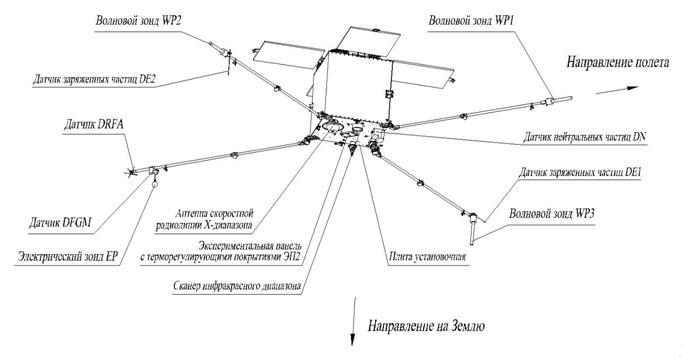
Spacecraft with booms (tentative layout)
To this, precise astro-sensor (allowing attitude determination within 0.01 deg.), gas engine and infra-red band remote sensing scanner are foreseen to install onboard.
Detailed information about the mission will be prepared after the final clarification of the payload composition and international team of project participants formation.
